Ecommerce has experienced significant growth in recent years, with more consumers than ever buying everything from groceries to furniture online. As technology advances, the future of ecommerce looks even brighter, offering faster delivery, personalized shopping, and AI-powered experiences.
However, physical stores aren’t going away. Many retailers are opening new locations, testing pop-up shops, and attracting customers who prefer the in-store experience. So, when considering retail vs ecommerce, which approach is best for your business: selling online, offline, or both?
This article explores the differences between retail vs ecommerce, current trends, and how to determine the best strategy for your business.
What is retail?

Retail is just the simple act of selling things directly to people. It could be clothes, groceries, electronics, you name it. If someone’s buying a product for their personal use (not to resell it), that’s retail.
We usually think of retail as walking into a store and buying something off the shelf. But it’s more than that now. It could be shopping online, using an app, or even ordering something through social media. Whether it’s your local corner shop or a huge online store, it all falls under retail.
At the end of the day, retail is about making it easy for people to find and buy what they need.
Types of Retail Models

| Types | Explanation |
| Brick-and-mortar stores | where customers can visit, browse products, and make purchases. |
| Department stores | Convenient for consumers to find various items in a single location. |
| Shopping malls | Large complexes feature numerous retail stores, along with movie theaters, restaurants, and other attractions, providing a comprehensive shopping experience. |
| Pop-up shops | Temporary retail spaces appear for a limited time, often in vacant storefronts or at events, allowing brands to create unique and immersive shopping experiences or test new markets. |
Understanding retail is essential for both consumers and businesses. It helps consumers make informed purchasing decisions and navigate the ever-changing retail landscape, while businesses can leverage this knowledge to create engaging shopping experiences and meet customer demands effectively.
What is Ecommerce?

Ecommerce is just buying and selling things online. Whether you’re shopping on a website, using an app, browsing social media, or checking out an online marketplace, it’s all part of ecommerce.
For example, it’s when you order something from an online store, pay for it digitally, bid on items in an online auction, or even handle your banking over the internet. The beauty of ecommerce is that you can engage in it from anywhere as long as you have an internet connection. For businesses, the main goal of ecommerce is to boost sales by utilizing digital marketing and online sales strategies.
Ecommerce is sometimes spelled ecommerce and is often used to describe everything involved in selling online, whether it’s creating digital ads or securely processing payment transactions over the internet.
Types of Ecommerce Models

| Types | Explanation |
| Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-commerce | Online platforms facilitate businesses in selling products or services directly to consumers. |
| Business-to-Business (B2B) E-commerce | It involves transactions between businesses, where one business sells products or services to another business. |
| Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) E-commerce | It involves consumers to sell products or services directly to other consumers through online platforms. |
| Mobile Commerce (m-commerce) | It involves transactions conducted through mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. |
| Social Commerce | It involves consumers selling products or services directly to other consumers through online platforms. |
| Dropshipping | where online retailers do not stock or handle the products they sell. |
| Subscription-Based E-commerce | It recurring payments for the continuous supply of products or services. |
Read More: To Know Briefly about Types of Ecommerce
What is the Difference Between Retail and Ecommerce?
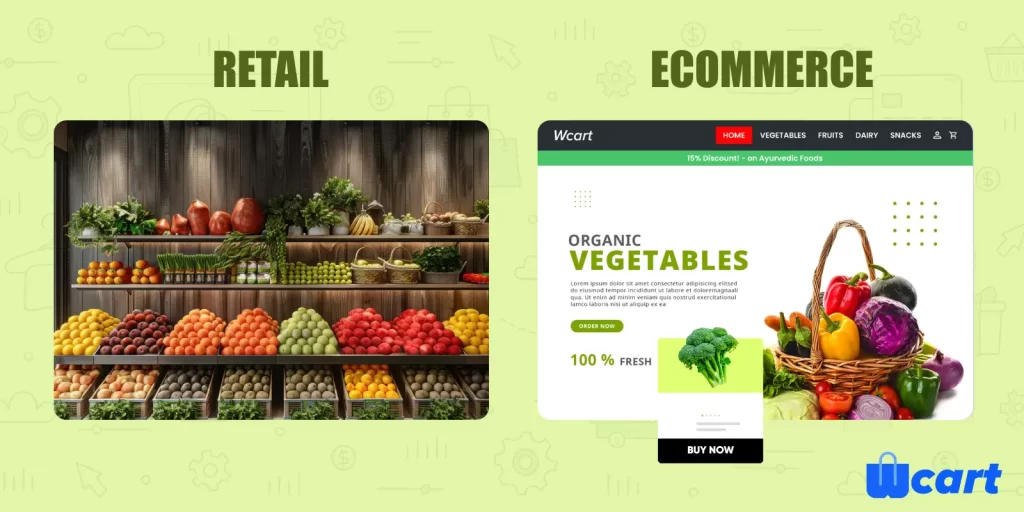
Retail is all about shopping in physical stores, where you interact with staff and make purchases in person.
Ecommerce, however, is shopping online, where you browse websites, make payments digitally, and often get things delivered directly to you.
Retail and ecommerce differ primarily in their environments, retail takes place in physical stores, while ecommerce happens online. Ecommerce typically has lower operating costs because it doesn’t require a physical storefront, which can result in better prices for consumers.
1. Brick-and-Mortar Presence vs. Online Presence

Retail:
- Retail operates through physical stores or establishments where customers can visit to browse and purchase products.
- It provides a tangible shopping experience, allowing customers to interact with products, seek assistance from sales personnel, and make immediate purchases.
Ecommerce:
- Ecommerce operates exclusively online, with transactions taking place through websites, online marketplaces, or mobile applications.
- It provides a virtual shopping experience, where customers browse through digital catalogs, view product images and descriptions, and make purchases electronically.
2. Geographic Reach

Retail:
- Retail stores are limited by their physical locations, targeting customers within a specific geographic area.
- Expansion beyond the local market requires opening new stores or establishing partnerships with other retailers.
Ecommerce:
- Ecommerce has a global reach, allowing businesses to target customers worldwide.
- Online platforms provide access to a vast customer base without the constraints of physical locations, enabling businesses to expand their reach more easily.
3. Operating Costs

Retail:
- Retail operations often require substantial upfront investments, including store setup, inventory management, staffing, and overhead costs.
- Costs are incurred for rent, utilities, store maintenance, and in-store marketing efforts.
Ecommerce:
- Ecommerce generally has lower overhead costs compared to retail, as it eliminates the need for physical stores.
- Initial investments are primarily focused on developing and maintaining an online platform, digital marketing, and order fulfillment infrastructure.
4. Customer Experience and Engagement

Retail:
- Retail stores offer a sensory and immersive shopping experience, allowing customers to physically examine products, try them on, or test their functionalities.
- Customers can receive immediate assistance from sales personnel and engage in face-to-face interactions.
Ecommerce:
- Ecommerce provides convenience and accessibility, allowing customers to shop from anywhere, at any time.
- Customers rely on product descriptions, images, customer reviews, and virtual assistance to make informed purchase decisions.
5. Inventory Management and Fulfillment

Retail:
- Retail stores require physical inventory, which needs to be stocked, managed, and displayed in-store.
- Customers can make immediate purchases and take products home with them.
Ecommerce:
- Ecommerce allows for centralized inventory management, with products stored in distribution centers or warehouses.
- Order fulfillment involves packaging, shipping, and delivery to customers’ doorsteps, often through shipping partners or in-house logistics.
6. Customer Service and Returns

Retail:
- Retail stores provide immediate customer service through in-person interactions, allowing for real-time issue resolution and returns/exchanges.
- Returns and exchanges can be processed directly in-store.
Ecommerce:
- Ecommerce offers customer service through online channels like chat support, email, or phone.
- Returns and exchanges often require shipping products back to the retailer, following specific return policies and procedures.
Understanding retail and ecommerce is crucial for businesses and consumers navigating the digital age. While retail offers tangible experiences and immediate customer service, ecommerce provides convenience, global reach, and cost efficiencies. The future lies in integrating online and offline channels to provide seamless customer experiences and adapt to evolving consumer expectations.
Read More: To Know about Ecommerce Trends
Ecommerce Vs Retail for consumers

When you shop in a store, you head out to a physical location, check out what’s available, talk to a salesperson if you need help, and then bring your stuff home.
Online shopping works a bit differently. You can either go straight to your go-to website, discover a new shop through an ad or social media, compare prices, buy what you need, and then wait for it to be delivered.
Choosing which one is better comes down to what kind of shopping experience you’re looking for, how much help you want from customer service, and what works best for your schedule.
Ecommerce Vs Retail for businesses

For business owners, deciding between a physical store and online sales depends on what they’re selling and who their customers are. Selling a few products on your own is very different from running a larger business that sells hundreds of products to a loyal customer base.
Choosing between a retail business and an ecommerce business comes down to a few key factors: how much you need to invest initially, the scale of your business, and whether you want to sell through different channels.
How Omnichannel Retailing Is Shaping the Future of Sales
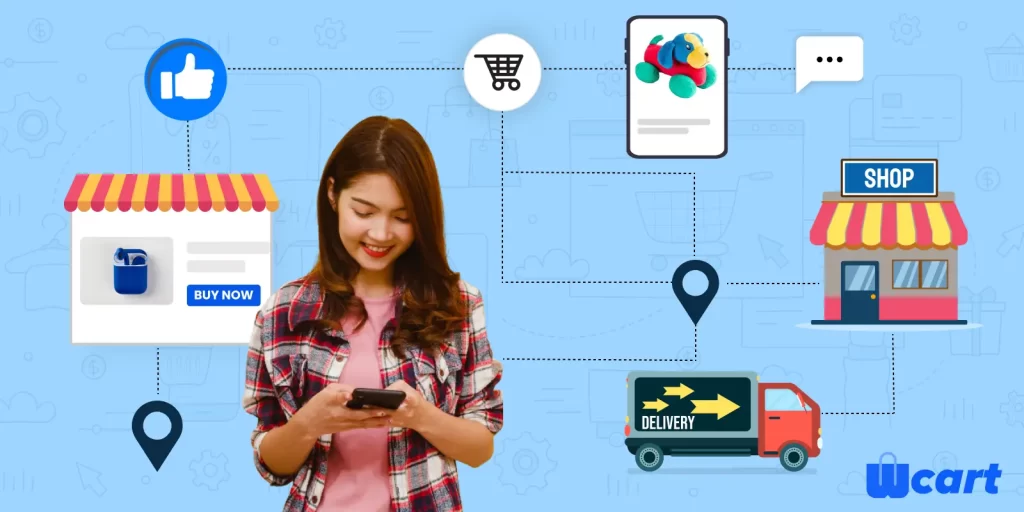

Omnichannel retailing transforms how businesses interact with customers by creating a seamless shopping experience across various platforms, whether online, in-store, mobile, or social media.
Rather than handling each channel individually, businesses are now combining each channel to offer a consistent and personalized experience rather than handling each channel individually. For example, customers can browse products on their phone, ask questions on social media, and complete their purchase in-store or online without any issues.
With growing consumer demand for convenience and speed, features like Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store (BOPIS), curbside pickup, and live inventory updates have become essential. Omnichannel strategies also give businesses better insights into customer behavior, allowing them to improve promotions, services, and inventory.
This leads to higher customer engagement, loyalty, and sales. In addition, it helps businesses stay competitive by embracing new technologies like AI and AR, making the shopping experience smarter and more connected.
Final Words
To wrap things up, the whole retail vs ecommerce debate isn’t about one replacing the other; it’s about how they’re coming together. Retail and ecommerce are blending, creating a smoother shopping experience for customers.
Retailers are adding online options to their physical stores, and ecommerce companies are testing out physical locations. With the rise of omnichannel shopping, click-and-collect, and data-driven strategies, businesses are adapting to meet consumer needs in new ways.
The future isn’t about picking one model, but about successfully merging both. Still unsure whether retail or ecommerce is right for you? Feel free to reach out, we’re here to help.




Leave a Reply